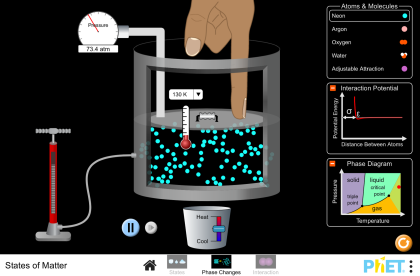
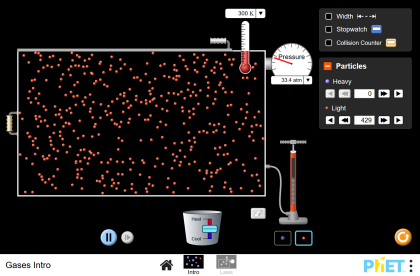
State Variables:
- volume (V), [m3]
- pressure (p), [Pa]
- mass (M), [kg]
- temperature (T) [K]: related to thermal energy (Eth)
- Derived: ρ = M/V (mass density) [kg m-3]
Molecules (分子) & Moles (摩爾mo2er3)
- N: Number of molecules [-]
- NA: 6.02214076 x 1023 [mol-1]
- n = N/NA [mol] (Why? For convenience)
Basic phases of matter and phase diagrams
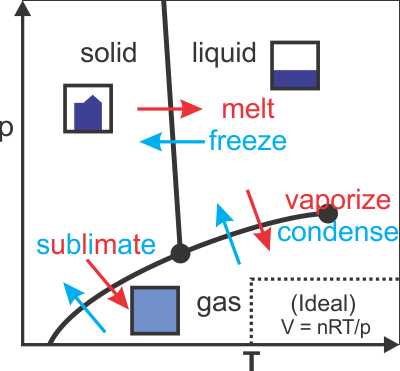
Ideal Gas Law
- Incompatable assumptions:
- molecules don't touch each other;
- gases in thermal equilibrium (requires contact)
- → Valid away from phase transition boundary (see phase diagram)
- Equation:.
- pV = n R T where R= 8.3144598 [J mol-1 K -1]
- pV = N kB T where kB=1.38064852 x 10-23 [J K -1]
pV diagrams used to illustrate Ideal Gas Law Processes
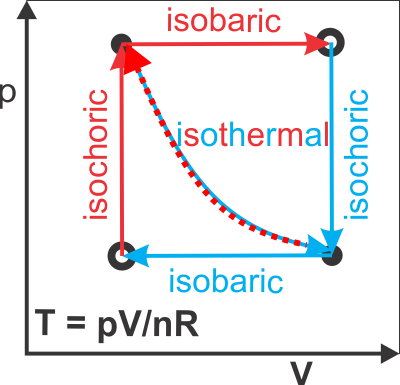
|
isochoric: Vf = Vi isobaric: pf = pi isothermal: Tf = Ti |
Lecture
Ref: Knight Version 4 Chapter 18FAQ

- Why are the the quantities such are R and NA not simple numbers? ANS: This is due to history and the way units were first defined. For example, we could define a new unit of temperature the [bai]. If 1 [bai] = 8.31 [K] then R=1. (Water would freeze at 32.87 bai, and boil at 44.8 bai. I could then define a scale for daily use T [xiaobai] = T[bai] -32.87 so that the freezing point of water would be 0 [xiaobai] and boiling point would be 11.9 [xiaobai] ) Similarily we could define a new unit of mass, the [white] such that so that Avrogadro's number is 1024!
- Why can we only consider quasi-static processes in thermodynamics? ANS: P,V and T are only defined for thermodynamic equilibrium. If things move fast we leave this equilibrium → the state variables are not defined. i.e. T is not constant in the system, P is not constant everywhere. To draw a path on the pV diagram we need to go ∞ slow. See Quasistatic and Reversible Processes (Khan Academy) for more information.